Applications: Biomedical
Our innovative imaging cameras employ advanced technology for enhanced clarity and detail in extensive tissue sample analysis.
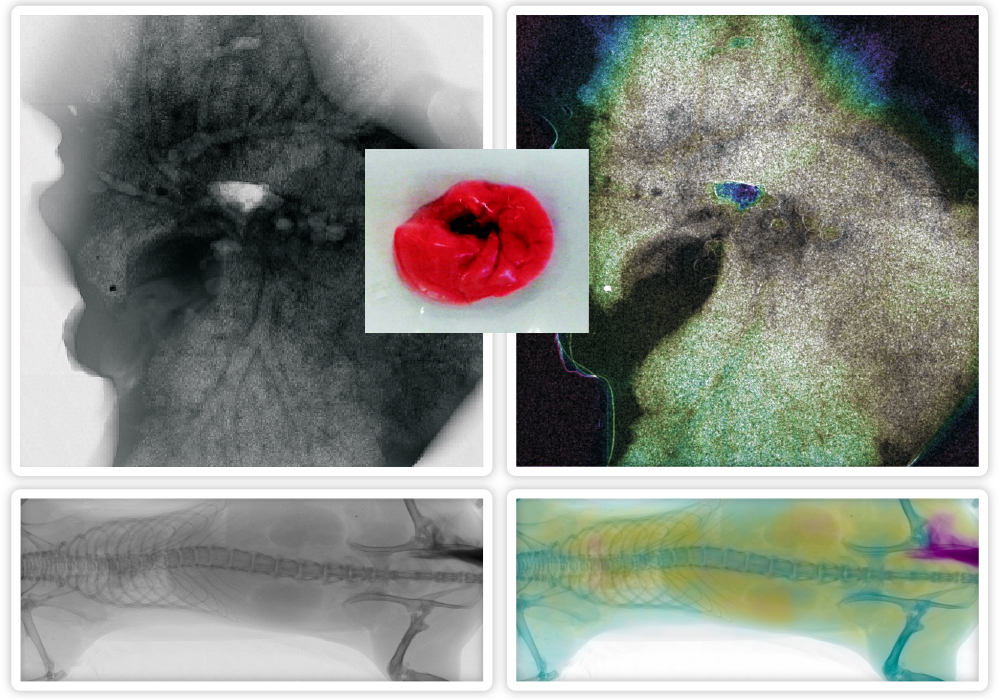
Our devices employ a unique blend of absorption imaging and phase contrast enhancement, allowing clear visualization of specific details in large tissue samples.
We have demonstrated this technology’s power by imaging a deflated mouse lung sample. Traditional imaging techniques struggled to differentiate between the granular structure of alveoli and other lung structures. Our advanced system, however, can distinguish alveoli and different tissue types and structures.
Our high-contrast X-ray system fine-tunes the X-ray beam spectrum and detector energy sensitivity levels to generate detailed images. This technology is a potent tool for tissue analysis, revealing features typically hidden due to low contrast, thereby revolutionizing the study of lung microstructures.