Dosimeters (devices designed to measure the dose delivered by ionizing radiation) are typically calibrated in reference fields that are precisely defined. However, in real-life situations, the radiation field may deviate significantly from this reference, causing the dosimeter to significantly underestimate or overestimate the dose. For the correct and accurate functioning of dosimeters, it is therefore important to monitor and characterize changes in the radiation field compared to the references. This will be achieved by the AdvaDose monitoring device currently under development, which will be based on a configuration of detectors with ASIC chips from the Timepix family in combination with software that will process the data measured by the detector into user-friendly outputs – from signaling changes in the radiation field relative to the reference, to full spectral and directional characterization of the radiation field, including decomposition into individual particle components. The results measured by this device will be compared with simulations that will be performed as part of the project.
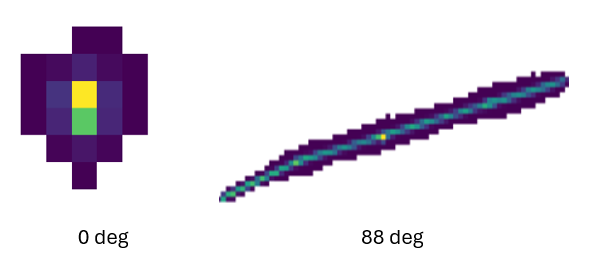
which arrive at the detector from different elevation angles (0 deg and 88 deg).
The AdvaDose monitoring device, whose detection unit can be configured for specific applications, will be suitable for both standalone use and implementation into existing solutions, where it will provide additional information needed for a more complete characterization of (mixed) radiation fields. Two such implementations will already take place within the project in the following devices:
- Stationary probes of monitoring networks: the introduction of the AdvaDose device will enable the monitoring of other types of radiation (alpha, beta, protons, heavy ions, etc.) that have not yet been monitored in these networks.
- Dosimetry devices for measuring radiation in aircraft: the integration of AdvaDose devices will ensure more comprehensive monitoring of the radiation exposure levels of flight crews.

